When hygiene matters most
The novel coronavirus, also known as SARS-CoV-2, is spreading worldwide. The main human-to-human transmission pathway appears to be droplet infection. With simple hygiene measures, each individual can help to protect themselves and others from the life-threatening lung disease and stem its rapid spread. This web information is dedicated to the most effective methods of protection against infection.
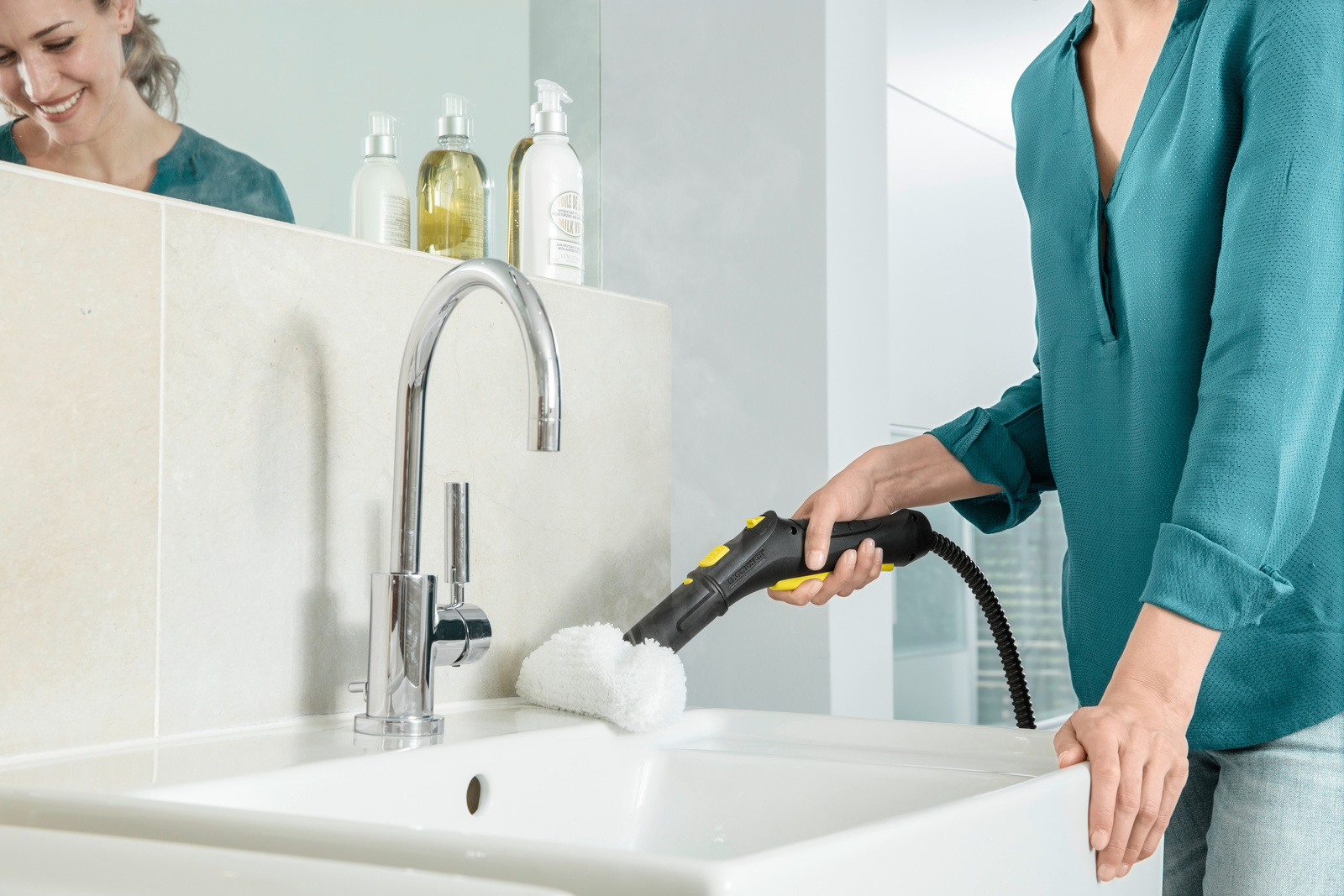


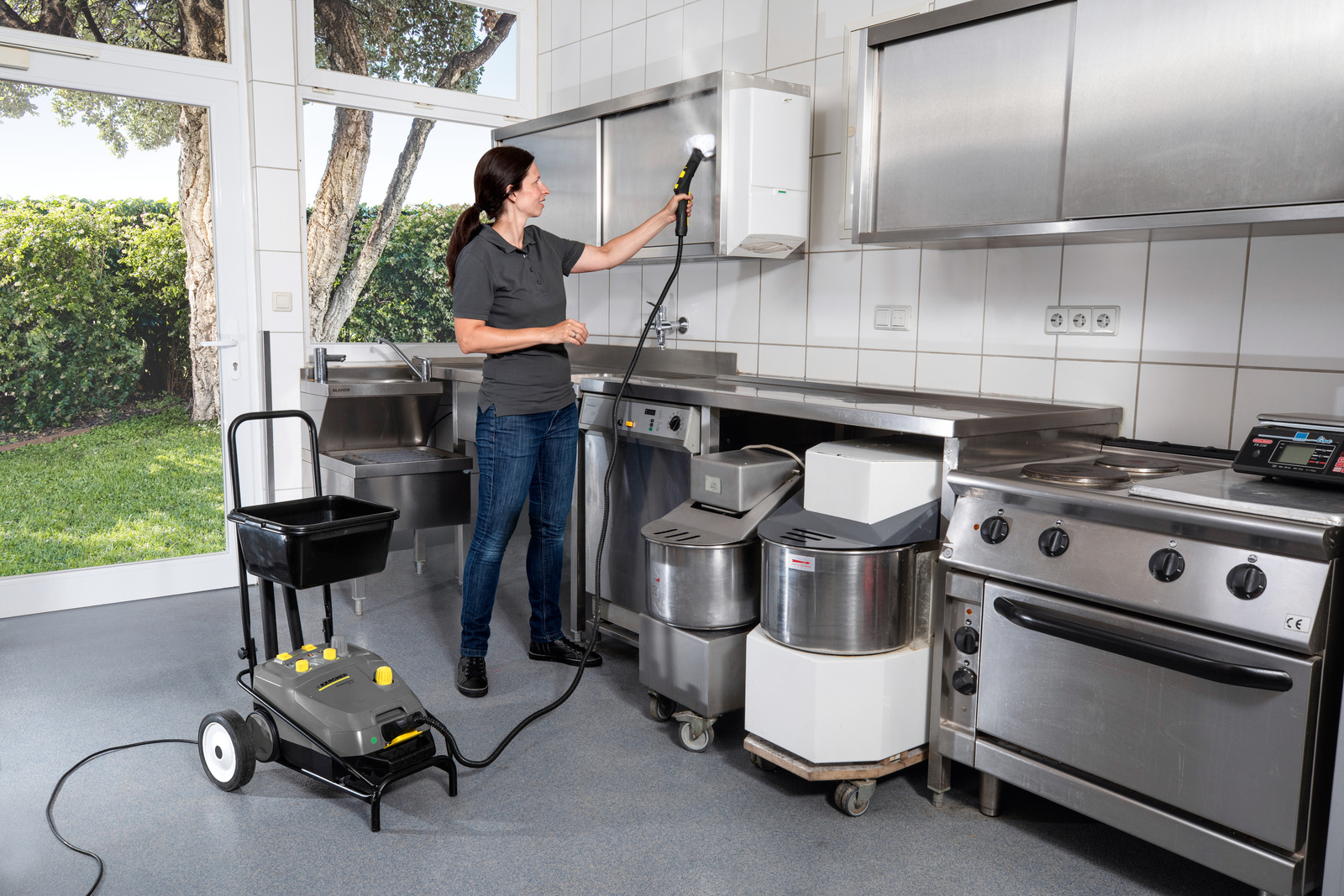
Kärcher steam cleaners to combat viruses, such as coronavirus
Kärcher arranged to have its steam cleaners tested in an independent laboratory for effectiveness in fighting viruses.
The result: if used properly, the machines remove up to 99.999% of enveloped viruses*, such as the coronavirus or influenza, and 99.99% of common household bacteria** from hard surfaces. At the present time, disinfectants are to be reserved primarily for outpatient and inpatient care, but steam cleaners can make a valuable contribution to general hygiene – both in private households and in commercial and industrial use.
*Tests have shown that with spot cleaning of 30 secs at max. steam level with the Kärcher home steam cleaner 99.999% of enveloped viruses such as coronavirus or influenza (excluding the Hepatitis-B virus) can be removed on typical household smooth, hard surfaces (test-germ: Modified-Vaccinia-Ankara-Virus).
**When thoroughly cleaning with the Kärcher steam cleaner 99.99% of all common household bacteria will be killed on typcial household smooth, hard surfaces, provided the cleaning speed of 30 cm/s at max. steam setting (test-germ: Enterococcus hirae). With Kärcher professional steam cleaners SG(V) this is 99.999%, according to EN 16615:2015-06, on PVC floors. (test germ: Enterococcus hirae ATCC 10541).
The laboratory test
Kärcher tested steam cleaners for domestic use as well as machines for professional use. Whether the steam is produced in a boiler or in a water heater, it doesn't affect the result in combating the virus; both technologies achieved a comparable result in the laboratory.
Enveloped viruses such as the coronavirus can be neutralised with high temperatures. As viruses are not germs or living organisms, experts also talk about virus inactivation.
In the laboratory a certified test virus (Modified-Vaccinia-Ankara-Virus), which is representative for enveloped viruses, was distributed on a hard surface. This area was then cleaned with the hand nozzle of a steam cleaner and the appropriate microfibre pad. It was demonstrated that a significant reduction of up to 99.999% of the viruses could be achieved at maximum steam pressure and with a cleaning duration of 30 seconds on one area.

Where does the Coronavirus come from?
On 11 March 2020 COVID-19 was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The lung disease is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In contrast to an epidemic, the occurrence of an infectious disease in a pandemic is not localized and can spread across the entire globe, as can currently be observed. An infection with the coronavirus manifests itself through flu-like symptoms such as coughing, fever, rhinitis and fatigue. Breathing problems, neck scratches, headaches and aching limbs, nausea, diarrhoea and chills are also possible. The course of the disease is individually different and varies greatly. Symptomless progressions are possible, as well as severe pneumonia with lung failure and death. Researchers assume that the corona pathogen SARS-CoV-2 was transmitted from a wild animal to a human being at a food market in the Chinese city of Wuhan (Hubei province). However, which animal originally carried the virus has not yet been clarified beyond doubt. At present, it is assumed that the pathogen was first transmitted from bats to other animals before it spread to humans - presumably by eating an animal that served as an intermediate host for the SARS-CoV-2 pathogen and was offered for sale at the market.
Trigger of infectious diseases
Infectious diseases can be caused by various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria or fungi.
How is the Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 transmitted?
Droplet infection:
According to expert information available at this time, the corona pathogen SARS-CoV-2 is primarily transmitted via the so-called droplet infection. This involves people coughing or sneezing and distributing the pathogens in the air. Other people inhale these pathogens and, in the worst case, become infected with them as well.
Indirect infection:
Indirect transmission of the virus is also possible. People who have previously coughed or sneezed into their hands touch objects such as door handles, mobile phones, touch screens or chair backs spreading infection. The viruses remain on the surface and reach healthy people from there.
Contact infection (smear infection):
Smear infection is also a way for viral diseases to spread. For example, even the smallest, contaminated residual traces of human stool can reach a healthy person via dirty hands. Infection is also possible if the pathogen enters the body directly via the mucous membranes of the eyes, throat and nose or the upper airways, for example through a kiss. It has not yet been finally clarified whether SARS-CoV-2 spreads via a smear infection. One of the most effective measures to prevent smear infection is to wash your hands thoroughly with standard soap.
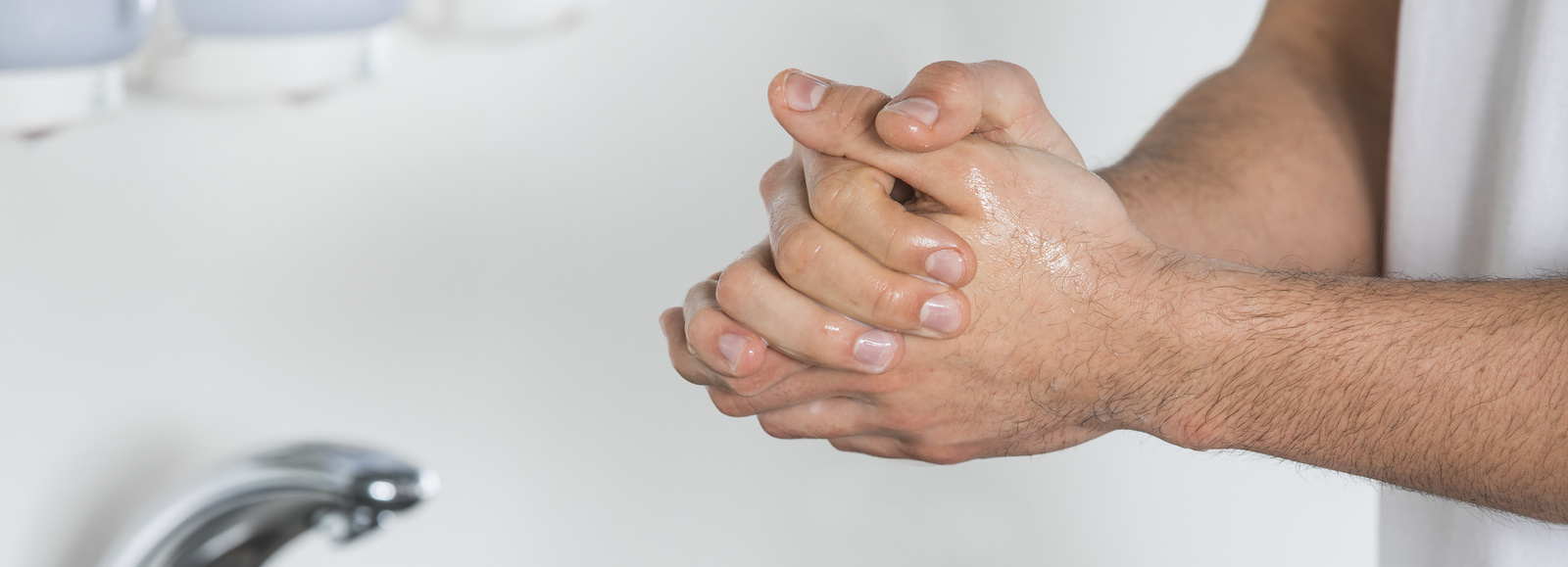

How can you protect yourself and others from infection?
Since there is currently no vaccine against the coronavirus, it is very important to follow simple hygiene measures - both in personal hygiene and in public spaces.
Why hygiene measures are so important in times of Corona
In a hygienic, well-maintained environment that is cleaned regularly, the risk of transmission of pathogens is minimised considerably. Surfaces are no longer a breeding ground for germs, bacteria or viruses. Even in places that are difficult to access, the pathogens are eliminated more thoroughly.
Read on:
Cleaning measures for cleanliness and hygiene at home and in public places.