Setting up a wash bay
Wash bays for your own use are indispensable for vehicle workshops. They are needed for vehicle care, for washing parts and for cleaning customer vehicles. At the same time, the wash bay must be environmentally compatible, safe and efficient. This can be achieved only with detailed and careful planning – from the construction to the technical equipment.
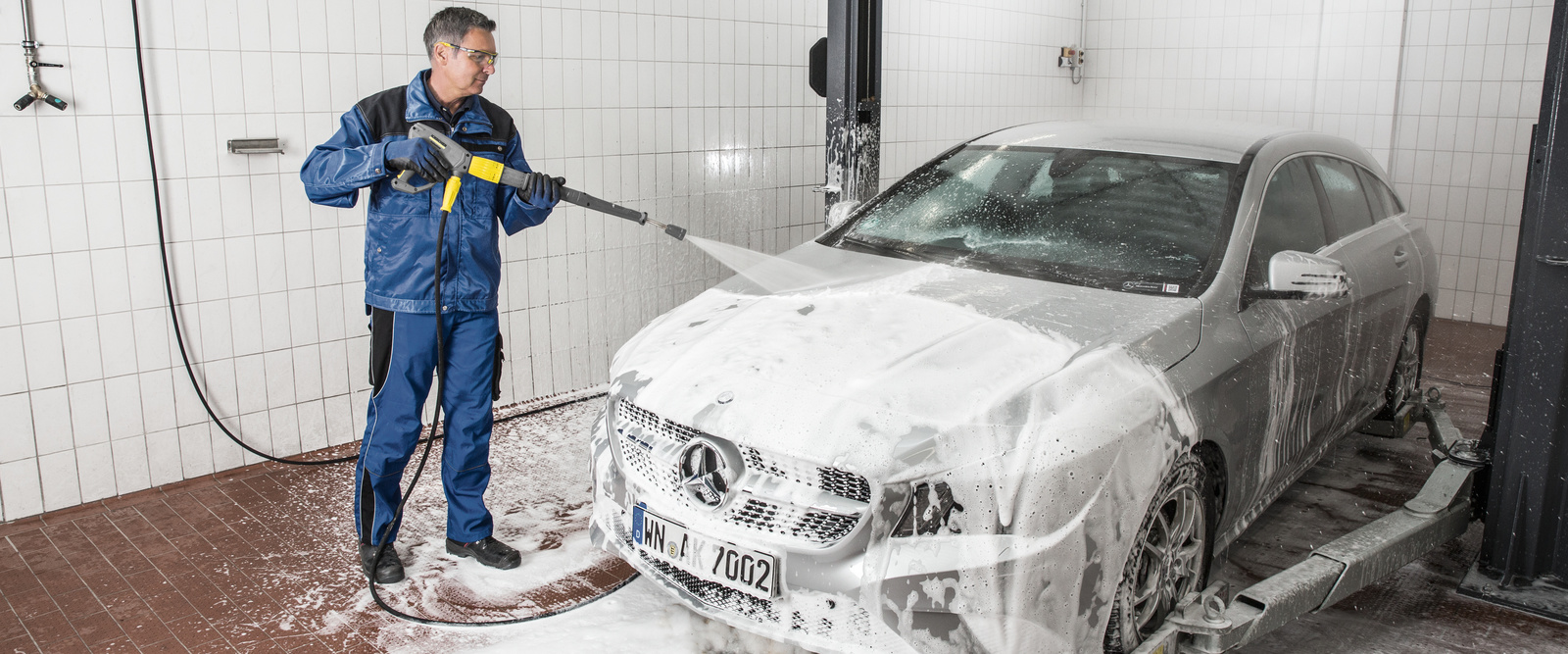

Requirements and equipment: Quick and reliable in your own wash bay
Experience shows that vehicle workshop wash bays, once they have been set up, are used several times practically every day by all the workshop employees. Good washing results also have a direct effect on the quality of work in the workshop. In this way, a vehicle workshop wash bay makes an essential contribution to customer satisfaction, helping to ensure customer loyalty and attract new customers.
Requirements and operation of wash bays in workshops
Anyone wanting to set up a new workshop wash bay must first take care of the water management and construction permits. The main condition for the operation of a vehicle wash bay is the "discharge permit" for waste water produced during cleaning, which must be applied for from the water authority. In addition, a valid construction and operation permit must be obtained. In event of the renovation of existing vehicle wash systems or wash bays, it is only necessary to inform the respective authority.
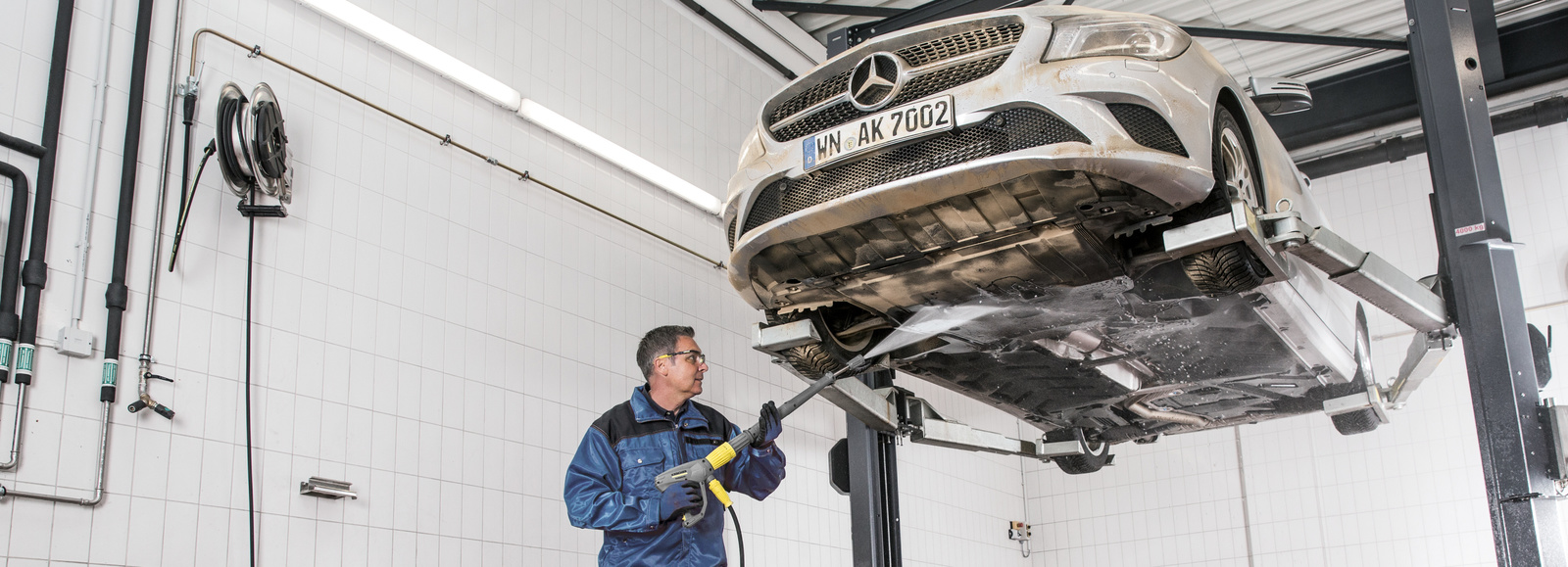

Construction requirements for wash bays
When the necessary permits have been obtained, special requirements concerning the structural design of the wash bay must be observed, for example the separation of washing water and rainwater. It must be ensured, for example, that, in the case of uncovered wash bays, no rainwater or melt water from neighbouring areas flows into the wash bay. Otherwise there is the risk that the waste water separation systems may be overloaded. In turn, this means that the design of the ground plate of the wash bay must ensure a sufficient gradient towards the drain. Under no circumstances must washing water seep into the ground or into bodies of water outside of the wash bay. It must be possible to drive vehicles over the wash bay drain itself. For the creation of a liquid-tight ground plate that is resistant to mechanical stresses, waterproof concrete (e.g.: B 25/WU) or asphalt is permitted as in road construction. Important: Existing wash bays must be regularly examined by means of a visual inspection for cracks or other damage. If the ground plate is damaged, it must be sealed in accordance with professional standards immediately.

Waste water treatment: Sludge trap, light liquid separator, oil separator, etc.
Furthermore, every wash bay requires a sludge trap, in which suspended matter carried along in the washing water can settle. A pre-sludge trap for the coarse separation of significant amounts of suspended matter is usually located upstream of the sludge trap. It reduces the cleaning and disposal efforts required, so its additional cost is quickly cancelled out. A light liquid separator for oils and fuels must also be provided, which must be equipped with an inspection or control shaft for the regular inspection of the waste water. The wash bay also requires a coalescence separator for the treatment of emulsified liquids.

Noise protection for wash bays in workshops
Finally, the local noise pollution caused by the operation of the wash bay must also be checked. However, any disturbance of local residents can easily be minimised by noise protection installations. When all of these conditions have been met, the cleaning technology itself can be considered.

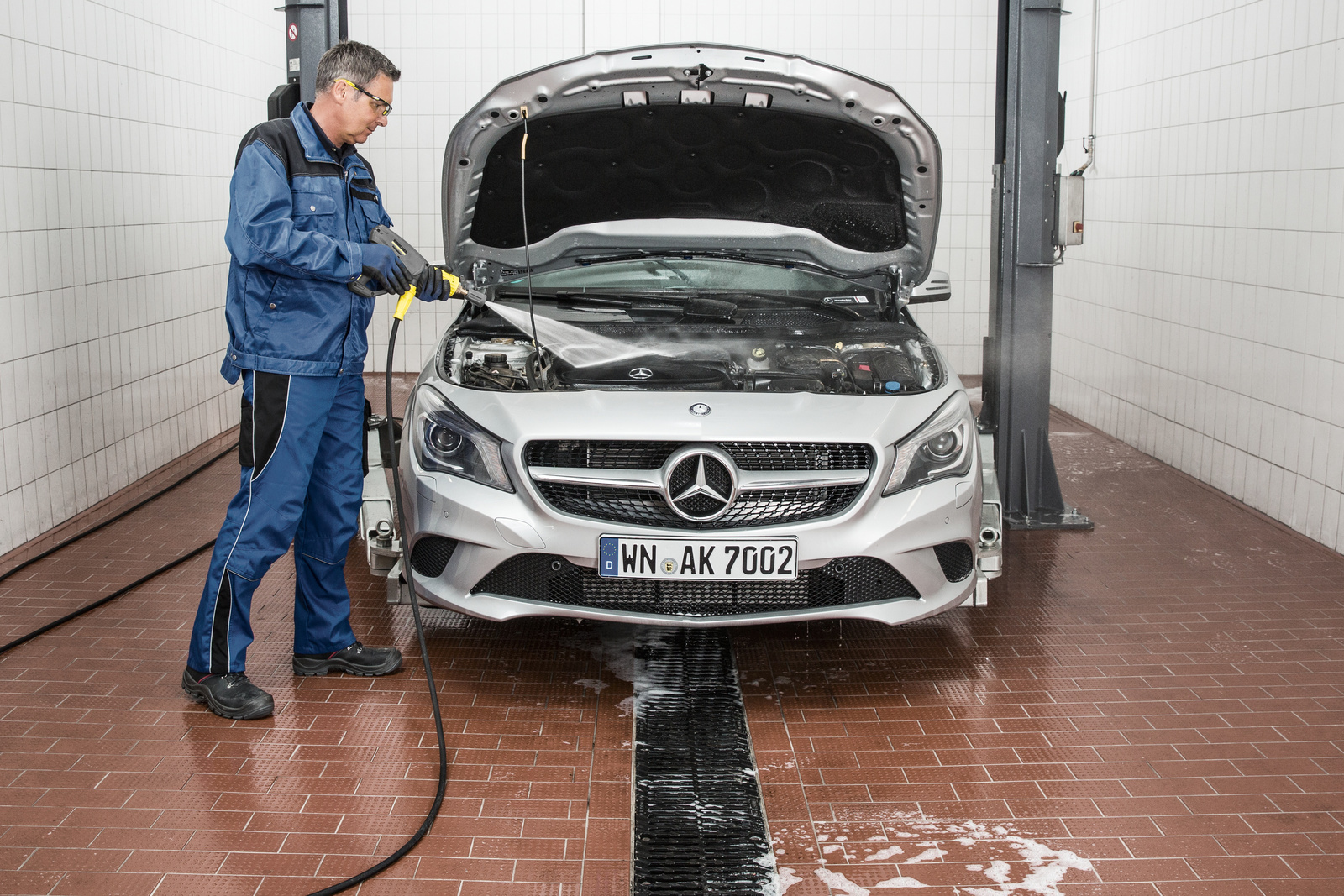
Selection of cleaning technology for wash bays: Stationary or mobile?
At wash bays that are not used for contract cleaning, cold- and/or hot water high-pressure cleaners are usually used. Here there is a choice between stationary and mobile machines.
Stationary high-pressure cleaners
If all the workshop personnel are to have access to the wash bay, the washing technology must be designed so that it is self-explanatory in order to exclude the possibility of operational errors. Here, a stationary high-pressure cleaner is the more appropriate choice compared with mobile machines, especially where the required space is available. The advantage is that the machine can be installed in a technology room that is not accessible to everybody. There, the employee responsible for the washing technology can set the type of programme, jet pressure, dosing of the washing chemicals and the duration of the washing time on the machine. These different pre-set washing programmes can be activated via a separate control terminal at the wash bay. Work accidents are thus avoided, regardless of how many employees use the wash bay, and damage to customer vehicles and parts caused by less experienced workshop personnel is prevented. Furthermore, on account of the shorter set-up times, stationary high-pressure cleaners are recommended wherever the wash bay is in operation for several hours each day and a large number of vehicles and parts have to be cleaned.
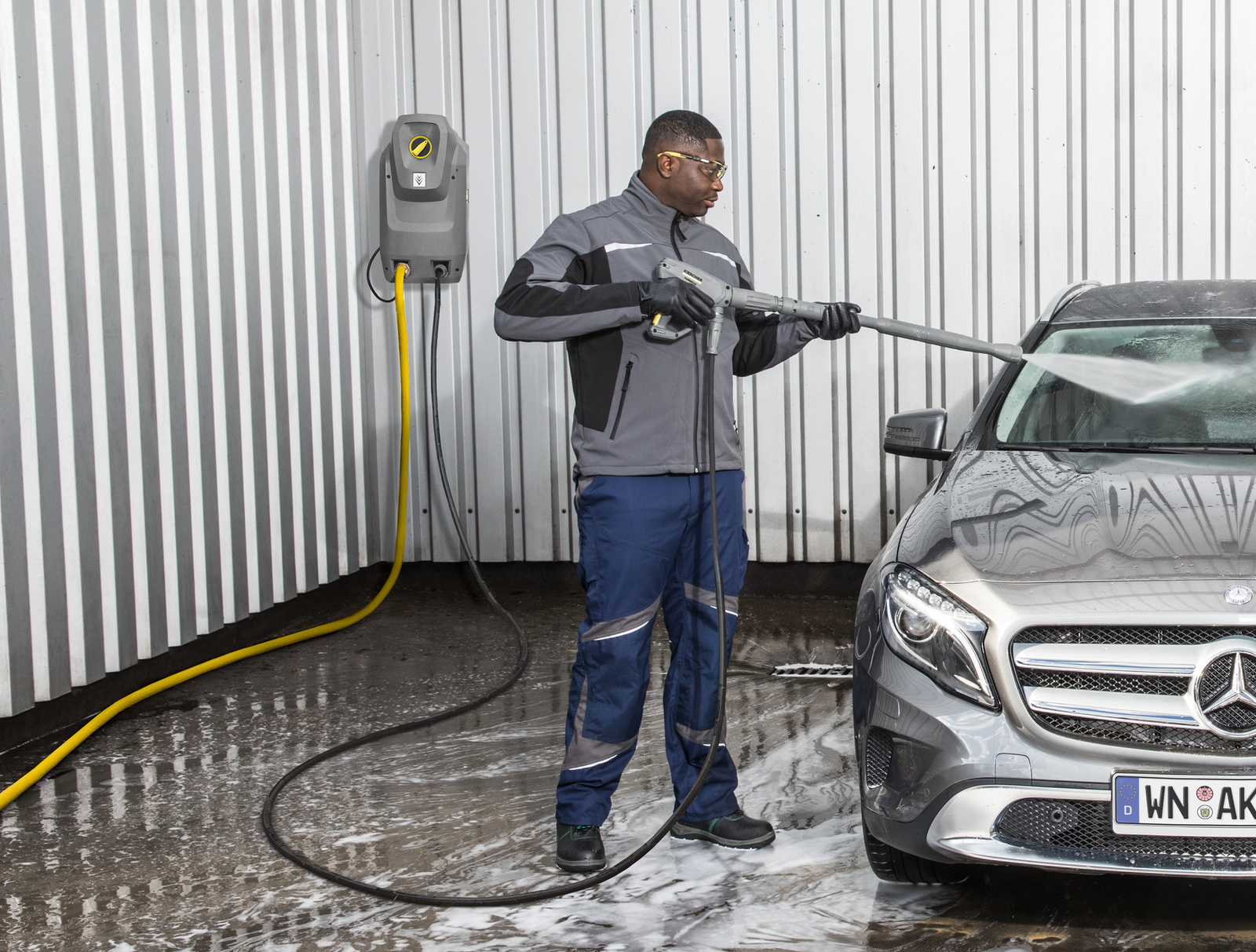

Mobile high-pressure cleaners
If the wash bay is used only occasionally, for smaller workshops a mobile cold or hot water high-pressure cleaner is sufficient for washing parts or vehicles. Depending on the available infrastructure and the requirements concerning performance, the high-pressure cleaners can be operated with electricity or with petrol or diesel. Their advantage is that they take up little space, as a special technology room is not required. However, mobile machines always involve longer set-up times. In addition, there is a certain risk of accidents caused by power lines, water hoses and high-pressure hoses lying around.
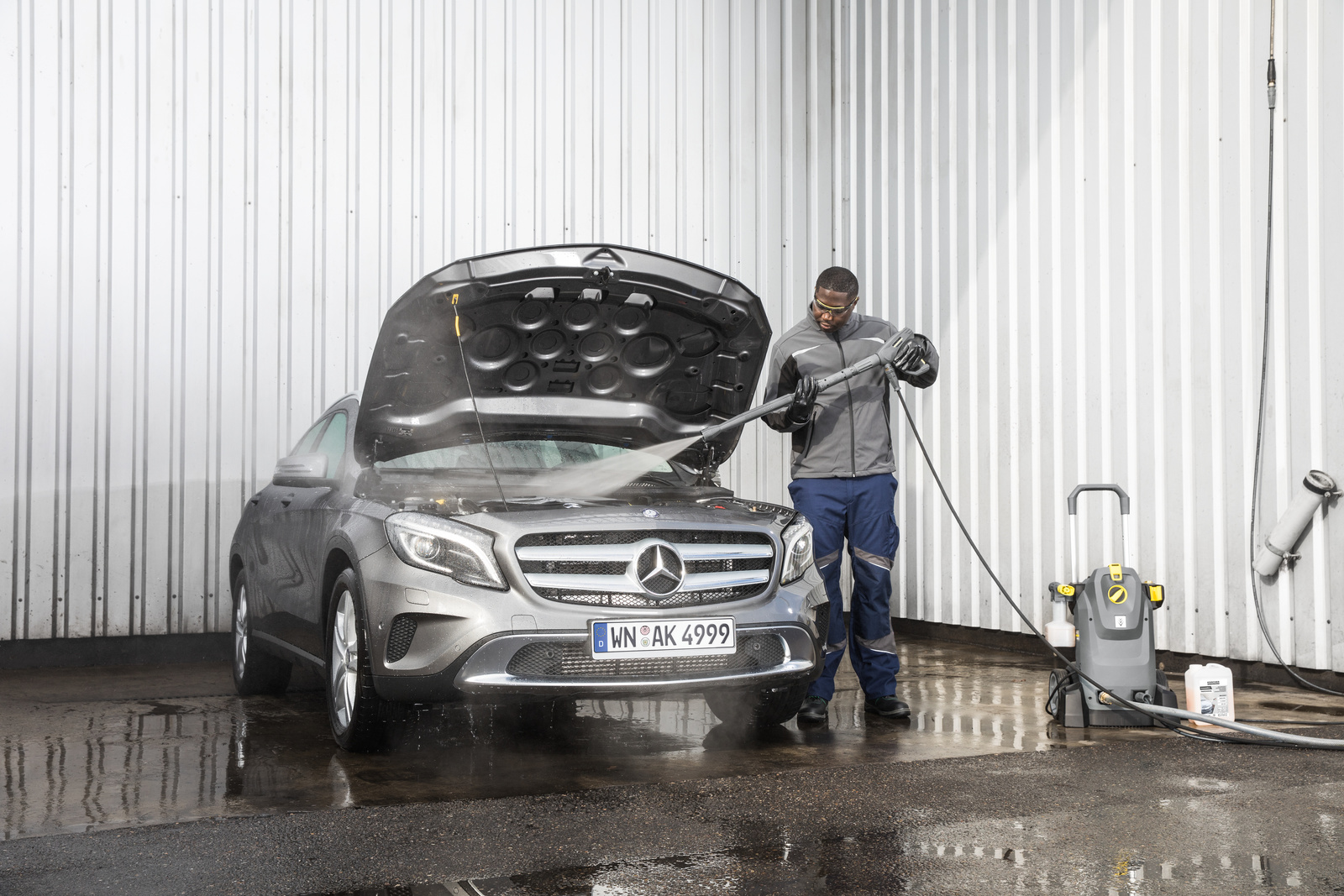
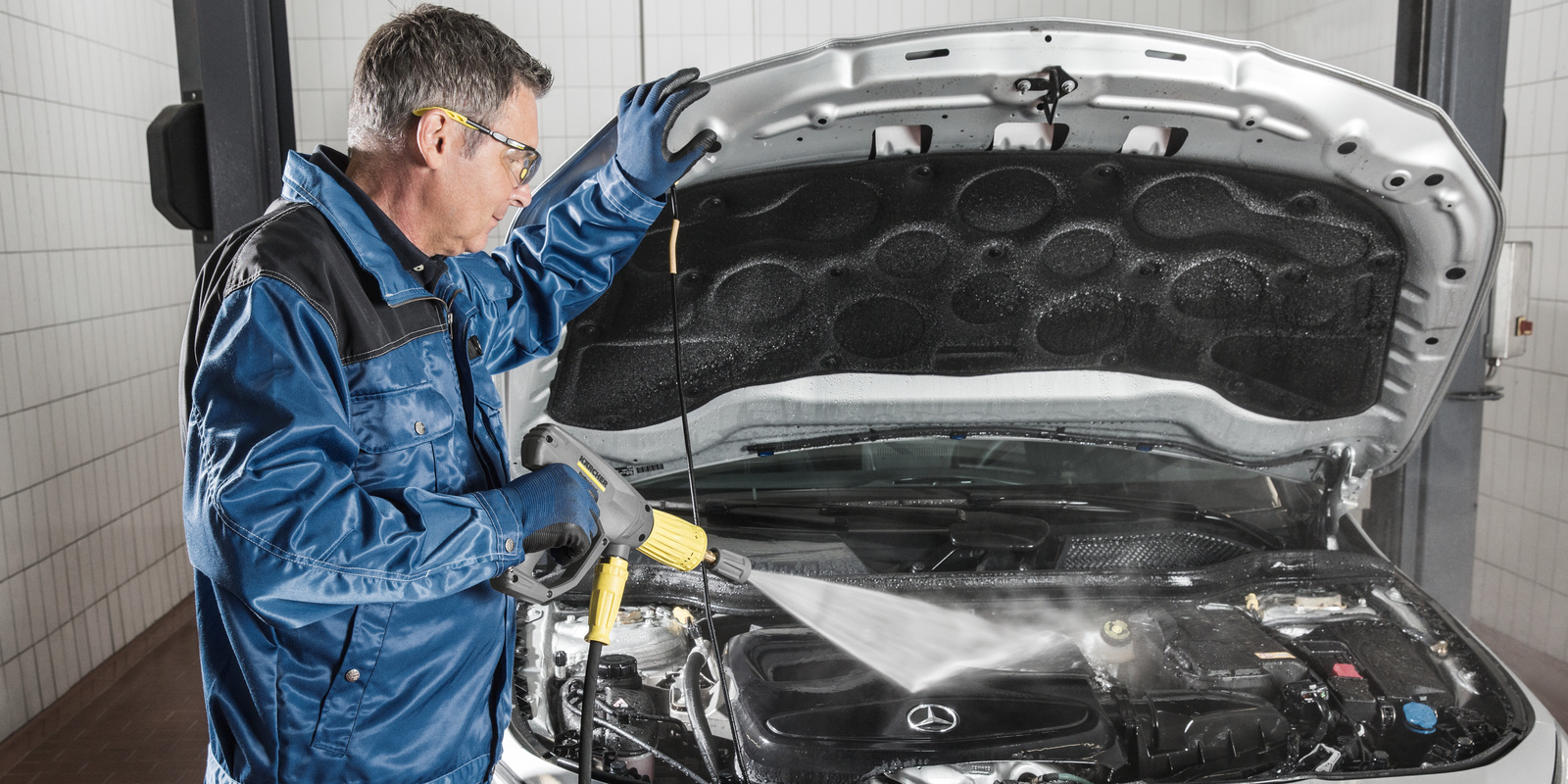


Cold, hot, steam
For the selection of the appropriate cleaning technology, the question arises as to whether the high-pressure cleaner is unheated or should be equipped with an oil or gas burner or an electrical water heater. To answer this question, the workshop infrastructure − the electricity, gas or oil supply − and its efficiency must be considered. If gas or oil is used to heat the water, a connection to a chimney must be available for stationary machines. If also a large number of engine washes are to be carried out, a hot water high-pressure cleaner with an additional steam stage must be considered. However, such machines must be used only by trained personnel on account of the risk of accident. Cold water machines, on the other hand, are suitable for washing the car body. In the summer, they cool hot parts of the car body, so that the washing water does not evaporate and can loosen adhering dirt over a longer period.
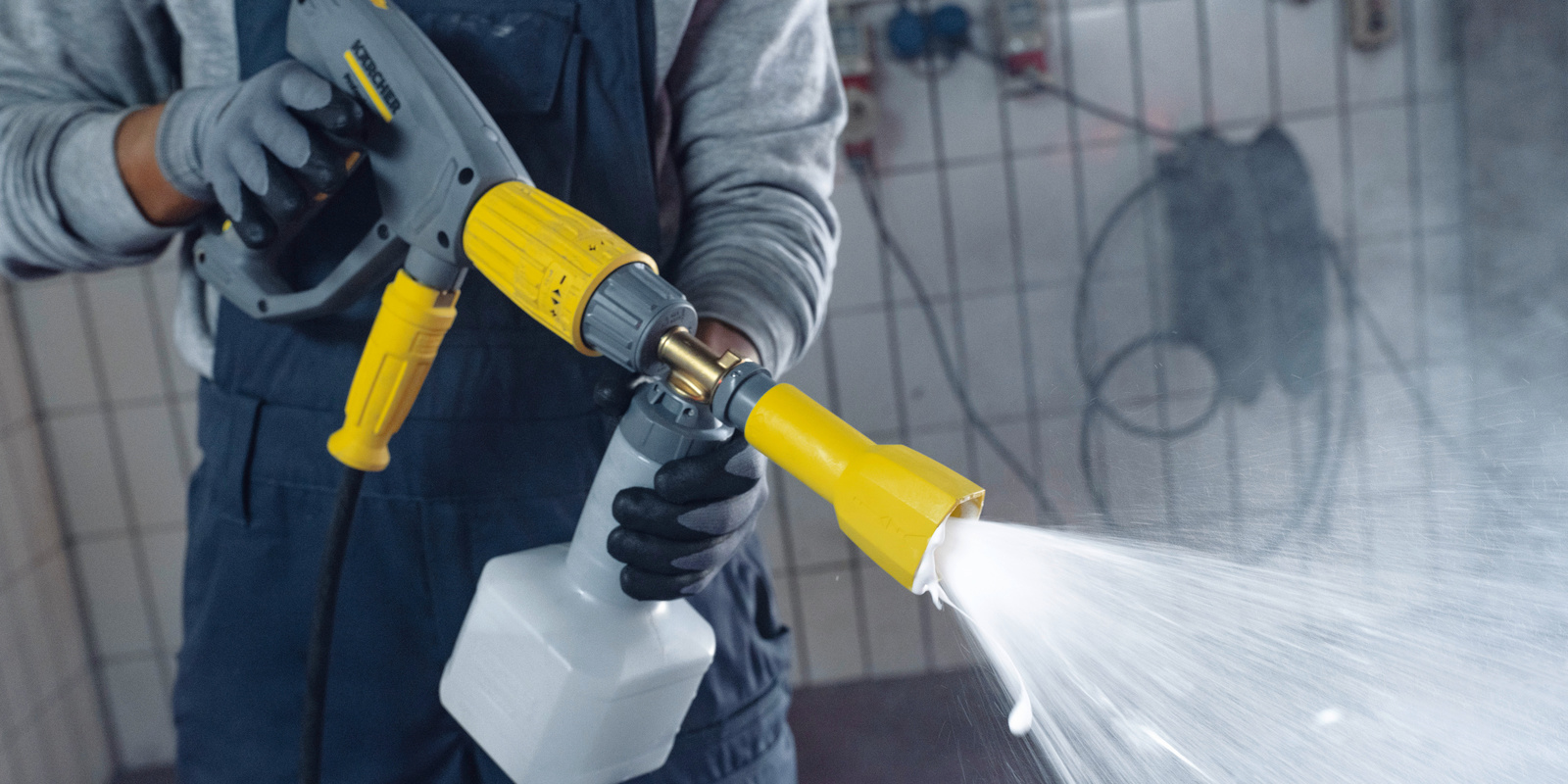

Cleaning agents
Ideally, the water pressure and temperature can be regulated at the lance or high-pressure cleaner according to the type of dirt, so oily or greasy dirt can be very easily removed by increasing the washing water temperature. In the case of very stubborn dirt, washing chemicals are additionally used. For this purpose, there are universal or special cleaners. Their use and regulation should be as simple as possible via the machine in order to prevent incorrect or excessive dosages. To ensure that the washing chemicals have no effect on the function of the light liquid or coalescence separator, the washing equipment manufacturers offer training or comprehensive instruction on their use. It is essential that use is made of these offers.
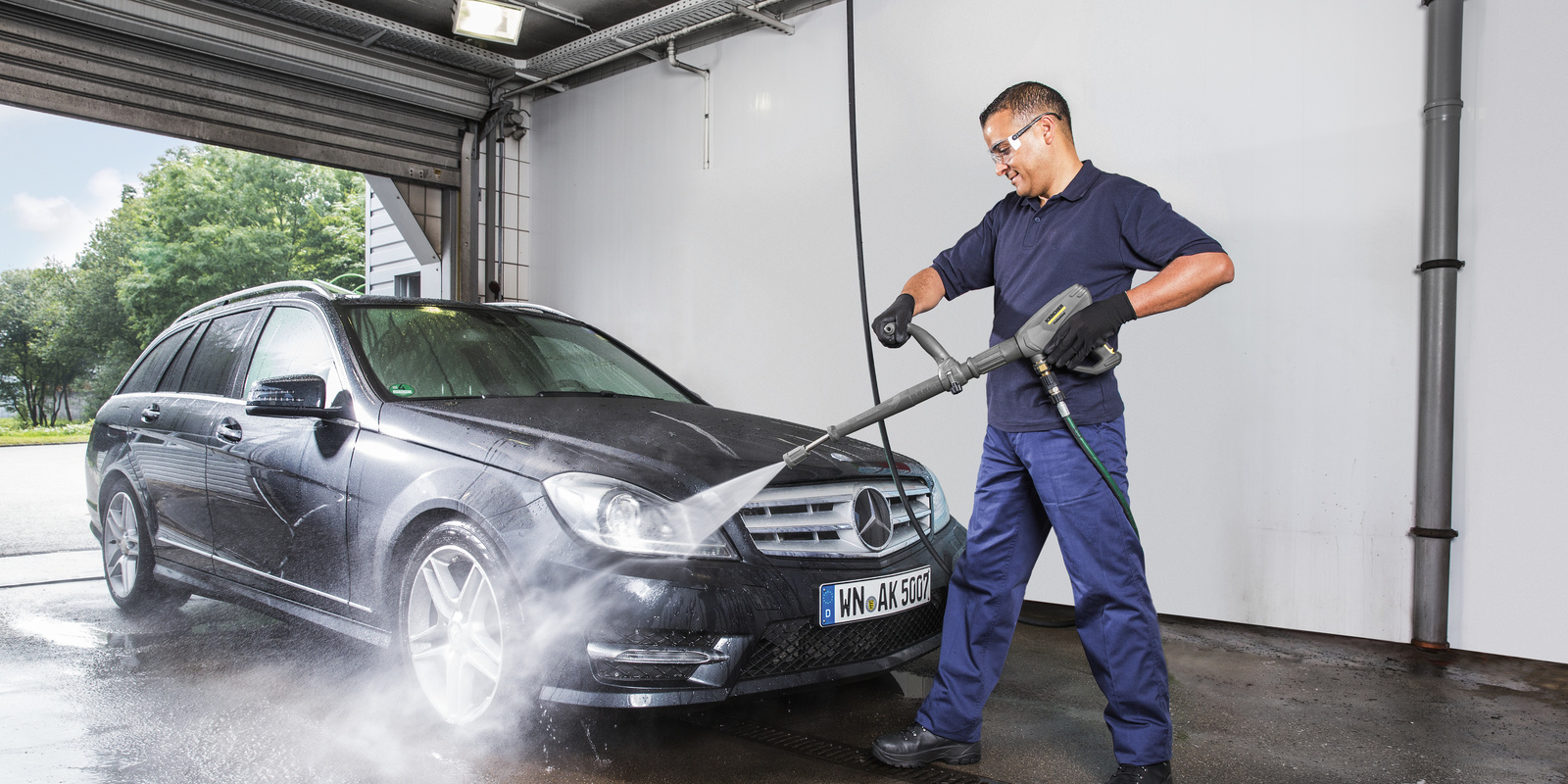

Ergonomics
Regardless of whether a stationary or mobile high-pressure cleaner is used, attention must be paid to the ergonomics of the tools and accessories. Physical injury caused by excessive, continuous strain can thus be reliably prevented. Symptoms of fatigue, which increase the probability of mistakes and therefore of injury, are also avoided.
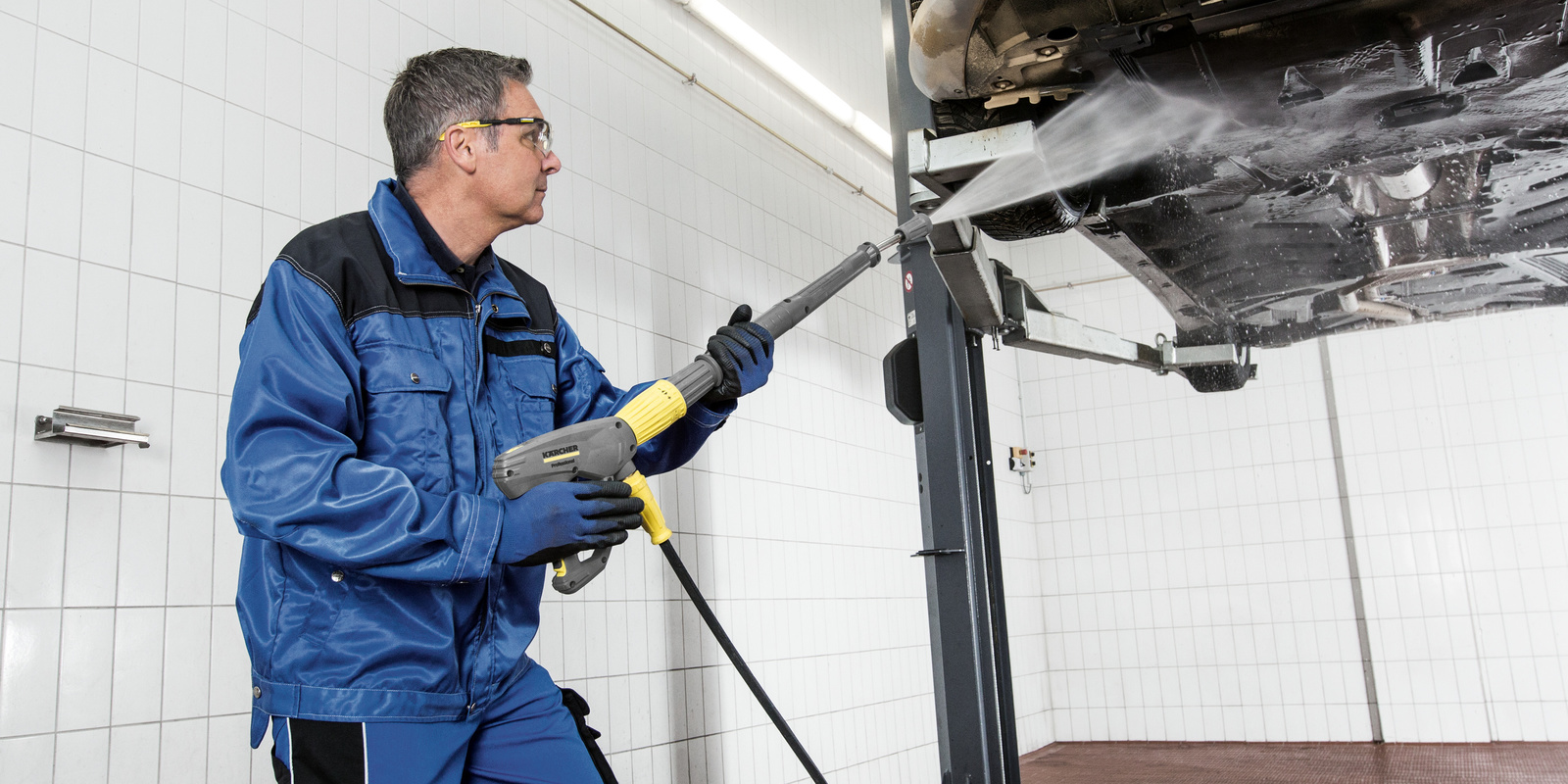

Accessories
The selection of accessories depends on the planned use and desired washing success. Foam lances, rotating wash brushes or articulated lances for underbody or roof washing are ideal for vehicle cleaning. Spray attachments with different spray angles, on the other hand, are preferably used for part washing.